In the intricate and shadowy world of digital finance and cybercrime, marketplaces dealing with stolen or fraudulent credit information operate silently but with tremendous scale and sophistication. One name that has savastan0 emerged as a leading player in this covert ecosystem is Savastan0—a marketplace primarily focused on the trade of credit BINs (Bank Identification Numbers). To understand how Savastan0 operates, why it matters, and what “BIN” really means in this context, we need to delve behind the scenes of this notorious digital marketplace.
What is a BIN, and Why Does It Matter?
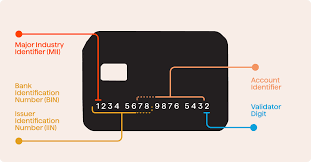
BIN stands for Bank Identification Number, which is the first 6 to 8 digits of a credit or debit card number. This sequence uniquely identifies the issuing bank or financial institution, card type, and sometimes geographic location. BINs are essential for routing transactions, verifying card authenticity, and managing fraud detection.
In legitimate commerce, BINs are a crucial component of payment processing. However, in the underground world, BINs are commoditized because they provide the foundational data for fraudsters to create or validate fake cards, test stolen card numbers, or execute card-not-present transactions.
For cybercriminals, possessing valid BIN information means they can target specific banks or card types that have vulnerabilities, making fraudulent transactions easier and less likely to trigger alarms.
What is Savastan0?
Savastan0 is a dark web marketplace that specializes in the trade of credit BINs, card details, and sometimes full dumps or CVV data. Unlike other broader dark web markets that offer a wide variety of illegal goods, Savastan0 has carved out a niche focusing on BINs sold in bulk, catering to fraudsters who want to operate at scale.
The marketplace is not openly accessible through the surface web and requires specific tools (like Tor) to access. It operates with a level of sophistication—complete with user reviews, tiered vendor rankings, escrow services, and sometimes even loyalty or discount programs—mimicking the features of legitimate e-commerce platforms to build trust among its illicit clientele.
How Does Savastan0 Work?
At its core, Savastan0 functions like an e-commerce platform but for illicit goods. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how the marketplace operates:
1. Vendors List BINs in Bulk
Vendors on Savastan0 specialize in sourcing, verifying, and packaging BINs in bulk. These packages typically include BINs linked to specific banks, regions, or card types (Visa, MasterCard, etc.). Some vendors savastan0.tools provide verified BINs that fraudsters can use with high confidence, while others offer “testing” or unverified BINs at lower prices.
2. Buyers Purchase and Verify
Buyers—mostly fraudsters or resellers—purchase these BIN packages. Once they have the BINs, they use them to create fake cards, validate stolen card numbers, or test transactions online. They may also combine BINs with other card data to perform unauthorized purchases or cashouts.
3. Escrow and Dispute Resolution
Savastan0 provides escrow services to ensure trust between buyers and sellers. Funds are held by the marketplace until the buyer confirms receipt of valid BINs. If there’s a dispute—say the BINs don’t work or are outdated—the marketplace often mediates, protecting both parties’ interests.
4. Reputation and Community
Vendors gain reputation points based on their reliability, speed, and product quality. Buyers leave reviews, helping the marketplace maintain standards and weed out scammers. This sense of community increases trust and promotes repeat business.
Why are BINs Sold at Scale?
One might wonder why fraudsters prefer buying BINs in bulk rather than individual card details. The answer lies in efficiency and the scale of operations:
- Mass Testing: With thousands of BINs, fraudsters can run automated scripts testing card numbers in bulk to find working combinations.
- Targeted Attacks: Certain BINs correspond to cards with higher credit limits or weaker security protocols. Fraudsters can target these for more profitable fraud.
- Supply Chain: BIN packages serve as building blocks. Once combined with additional stolen data (like CVVs or full card dumps), fraudsters can create usable fake cards or execute fraudulent online transactions.
- Reselling Potential: Some buyers of BIN packages resell the data or use it for phishing or other layered fraud schemes.
The Risks and Impact of Savastan0
Savastan0’s operations are not just a niche cybercrime problem; they have broad implications:
1. Financial Losses for Consumers and Banks
Stolen BINs facilitate fraud that can lead to unauthorized transactions, drained accounts, and identity theft. Banks bear significant costs in fraud prevention, chargebacks, and reimbursements.
2. Damage to Merchants
Merchants face losses from chargebacks and payment disputes resulting from fraudulent transactions. This can also damage their reputation and increase payment processing fees.
3. Legal and Ethical Concerns
The operation of Savastan0 is illegal worldwide. It undermines financial security and privacy and fuels a global black market that harms millions.
How is Savastan0 Different from Other Dark Web Markets?
While many dark web marketplaces exist, Savastan0’s specialization in BINs makes it unique:
- Niche Focus: Its singular focus on credit BINs and related financial data caters specifically to fraudsters who require large quantities of validated BINs.
- Sophistication: It offers advanced features like escrow, verified vendors, and buyer feedback, providing a more professional and trustworthy trading environment than many smaller or less organized markets.
- Scale: Savastan0 deals in bulk BIN sales, allowing for more extensive and efficient fraud operations than marketplaces that sell individual card details.
What Are the Security Measures Against Such Marketplaces?
Law enforcement agencies worldwide are continuously trying to combat marketplaces like Savastan0. Some of their strategies include:
- Dark Web Surveillance: Cybersecurity teams monitor dark web marketplaces to track sellers and buyers.
- Infiltration: Undercover operations attempt to penetrate these markets to identify key actors.
- Takedowns: Coordinated efforts between international agencies have led to the shutdown of many dark web markets, though new ones often replace them.
- Improved Payment Security: Banks and payment processors implement advanced fraud detection, tokenization, and multi-factor authentication to reduce BIN-based fraud.
The Future Outlook
The dark web and its marketplaces continue to evolve rapidly. Savastan0 exemplifies how specialized and streamlined cybercrime marketplaces have become. As financial systems advance, so do the methods of cybercriminals.
For consumers, it is crucial to practice good cyber hygiene—monitor bank statements, use secure payment methods, and be wary of phishing attempts. For organizations, investing in fraud detection and collaborating with law enforcement remain vital.
Conclusion
Savastan0 offers a window into the specialized and highly organized world of credit BIN marketplaces on the dark web. By focusing on the sale of BINs at scale, it empowers cybercriminals to operate efficiently and profitably in the digital underground.
Understanding how Savastan0 works “behind the BIN” sheds light on the broader challenges of financial cybersecurity today. While dark web marketplaces remain elusive and difficult to dismantle entirely, awareness, technological advancement, and vigilant enforcement can help reduce the damage they cause.
Staying informed is the first step in protecting yourself and the global financial ecosystem from these hidden threats.